Learn A – Z Linux commands cheat sheet with this comprehensive guide, complete with a free cheat sheet. Learn Linux and enhance your command-line skills.
In the vast realm of operating systems, Linux stands as a beacon of flexibility, efficiency, and robustness. Whether you are a seasoned system administrator or a curious enthusiast, mastering Linux commands is essential. This article serves as your ultimate guide to A – Z Linux commands cheat sheet, and to make your journey even smoother, we’ll throw in a free cheat sheet.
Linux commands cheat sheet are the building blocks of this open-source operating system. They allow you to interact with the system, manipulate files, configure settings, and perform a multitude of tasks. Here, we present a comprehensive list of Linux commands cheat sheet from A to Z, along with explanations and practical use cases.
Linux Commands Cheat Sheet 200+
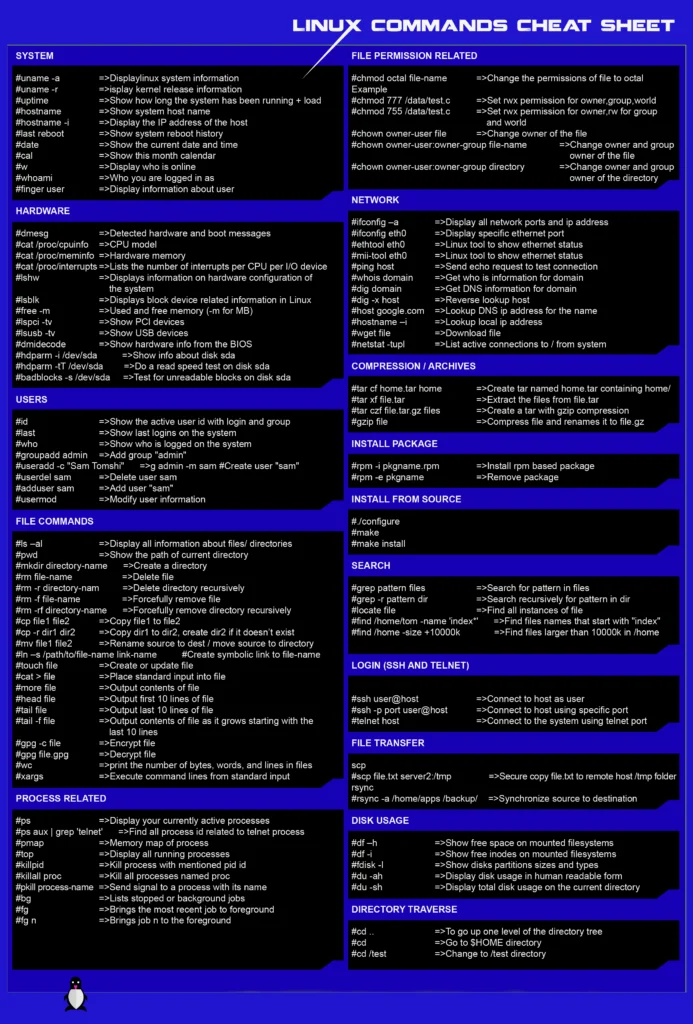
Navigation Commands
1: cd (Change Directory) : Navigate through directories.
2: pwd (Print Working Directory) : Display the current directory’s path.
3: ls (List) : List files and directories.
4: mkdir (Make Directory) : Create a new directory.
5: rmdir (Remove Directory) : Delete an empty directory.
File Operations
6: touch : Create an empty file.
7: cp (Copy) : Copy files and directories.
8: mv (Move) : Move or rename files and directories.
9: rm (Remove) : Delete files and directories.
10: cat (Concatenate) : Display and concatenate file contents.
System Information
11: uname : Show system information.
12: hostname : Display or set system hostname.
13: df (Disk Free) : Check disk space usage.
14: du (Disk Usage) : Show directory space usage.
15: top : Monitor system processes.
User Management
16: who : Display currently logged-in users.
17: useradd : Add a new user.
18: passwd : Change user password.
19: userdel : Delete a user.
20: su (Switch User) : Change the user context.
Package Management
21: apt-get : Advanced Package Tool for Debian-based systems.
22: yum : Package manager for RPM-based systems.
23: dpkg : Debian package manager.
24: rpm : RPM package manager.
25: yum install : Install software packages.
Networking
26: ifconfig : Configure network interfaces.
27: ping : Test network connectivity.
28: netstat : Display network statistics.
29: ssh (Secure Shell) : Securely access remote systems.
30: wget : Download files from the internet.
File Permissions
31: chmod (Change Mode) : Modify file permissions.
32: chown (Change Owner) : Change file ownership.
33: chgrp (Change Group) : Change group ownership.
34: umask : Set default permissions for new files.
35: sudo (Superuser Do) : Execute commands with superuser privileges.
Text Processing
36: grep (Global Regular Expression Print) : Search text using patterns.
37: sed (Stream Editor) : Streamline text editing tasks.
38: awk : Text processing tool for data extraction.
39: sort : Sort lines of text files.
40: cut : Remove sections from lines of files.
System Maintenance
41: shutdown : Shutdown or restart the system.
42: reboot : Reboot the system.
43: cron (Cron Jobs) : Schedule tasks to run at specified times.
44: tar (Tape Archive) : Archive files and directories.
45: find : Search for files and directories.
File Compression
46: zip : Compress files into a zip archive.
47: unzip : Extract files from a zip archive.
48: gzip : Compress files using gzip.
49: gunzip : Decompress gzip files.
50: tar -zcvf : Create a compressed tar archive.
Text Editors
51: nano : Lightweight text editor.
52: vi or vim : Powerful terminal-based text editor.
53: emacs : Extensible text editor.
54: gedit : GUI text editor for Linux.
55: leafpad : Simple notepad-like editor.
Process Control
56: ps (Process Status) : Display information about processes.
57: kill : Terminate processes.
58: nice : Set process priority.
59: nohup : Run commands immune to hangups.
60: bg and fg : Control background and foreground processes.
System Monitoring
61: htop : Interactive system monitor.
62: free : Display system memory usage.
63: iostat : Input/output statistics.
64: vmstat : Virtual memory statistics.
65: sar : System activity report.
Disk Management
66: fdisk : Disk partitioning utility.
67: mkfs (Make Filesystem) : Create a new filesystem.
68: mount and umount : Mount and unmount filesystems.
69: dd (Data Dump) : Copy and convert files and data.
70: badblocks : Scan for bad blocks on a disk.
Archive Management
71: tar -xvf : Extract files from a tar archive.
72: tar -jxvf : Extract files from a tar.gz archive.
73: tar -jcvf : Create a tar.gz archive.
74: tar -jxvf : Extract files from a tar.bz2 archive.
75: tar -jcvf : Create a tar.bz2 archive.
System Information
78: lshw : List hardware information.
79: lsblk : List block devices.
80: lspci : List PCI devices.
89: lsusb : List USB devices.
90: dmesg : Display kernel ring buffer messages.
System Updates
91: apt-get update : Update package lists.
92: apt-get upgrade : Upgrade installed packages.
93: yum update : Update packages (RPM-based systems).
94: dnf update : Upgrade packages (Fedora).
95: zypper update : Update packages (openSUSE).
Text Viewer
96: less : Display text files one page at a time.
97: more : Display text files page by page.
98: head and tail : Display the beginning or end of a file.
99: wc (Word Count) : Count words, lines, and characters in a file.
100: nl (Number Lines) : Add line numbers to a file.
Networking Tools
101: nc (Netcat) : Networking utility for reading/writing network connections.
102: telnet : Connect to remote hosts using the Telnet protocol.
103: traceroute : Trace the route to a host.
104: iptables : Configure firewall rules.
105: netcat : Network utility for sending and receiving data.
Package Queries
106: apt-cache : Query APT cache.
107: rpm -q : Query installed RPM packages.
108: dpkg -l : List installed packages.
109: yum list : List installed and available packages.
110: dnf list : List packages (Fedora).
Disk Usage Analysis
111: ncdu : Disk usage analyzer with an interactive interface.
112: du -sh : Display total disk usage for a directory.
113: df -h : Show disk space usage in a human-readable format.
114: ls -lh : List files with human-readable sizes.
115: tree : Display directory tree structure.
System Logs
116: journalctl : Query the systemd journal.
117: tail -f : Monitor log files in real-time.
118: grep -i error : Search for error messages in logs.
119: dmesg | grep error : Search kernel logs for errors.
120: /var/log : Explore system log files.
Network Configuration
121: ifconfig : Configure network interfaces.
122: ip : Display and manipulate network settings.
123: route : Show and modify the IP routing table.
124: netplan : Configure network settings (Ubuntu).
125: nmtui : Text-based network manager for Linux.
User Permissions
126: sudoers : Configure sudo access.
127: visudo : Edit the sudoers file safely.
128: su – : Switch to another user.
129: groups : Display group memberships.
130: chmod g+s : Set the setgid permission.
System Time
131: date : Display or set the system date and time.
132: timedatectl : Control system time and date.
133: hwclock : Manage the hardware clock.
134: ntpdate : Synchronize time with NTP servers.
135: at and batch : Schedule one-time or batch jobs.
Network File Sharing
136: samba: Configure Samba for file sharing.
137: nfs : Set up Network File System (NFS).
138: ftp : Transfer files using FTP.
139: scp (Secure Copy) : Securely copy files over SSH.
140: rsync : Efficiently sync files and directories.
System Backup
141: rsnapshot : Create backups using rsync.
142: tar -cvpzf : Create compressed tar backups.
143: dd : Create disk and partition backups.
144: Amanda : Advanced Maryland Automatic Network Disk Archiver.
145: Bacula : Set up network backups with Bacula.
Shell Scripting
146: bash : The Bourne Again Shell.
147: chmod +x : Make a script executable.
148: ./script.sh : Run a shell script.
149: $PATH : Understanding the path variable.
150: for and while loops : Create loops in shell scripts.
System Performance
151: vmstat : Report virtual memory statistics.
152: iostat : Display CPU and disk I/O statistics.
153: sar : Collect and report system activity data.
154: mpstat : Display CPU utilization statistics.
155: nmon : Monitor system performance interactively.
Text Manipulation
156: cut -d : Specify delimiter for text processing.
157: paste : Merge lines from multiple files.
158: comm : Compare sorted files line by line.
159: sort -u : Sort and remove duplicate lines.
160: awk -F : Set field separator for awk.
System Environment
161: env : Display environment variables.
162: export : Set environment variables.
163: echo $PATH : View the PATH variable.
164: source : Execute commands from a file.
165: set : Display shell variables.
System Information Tools
166: lscpu : Display CPU information.
167: lsusb : List USB devices.
168: lspci : List PCI devices.
169: lsscsi : List SCSI devices.
170: lsmod : List loaded kernel modules.
System Tuning
171: sysctl : View and modify kernel parameters.
172: ulimit : Set user-level resource limits.
173: nice and renice : Set process priority.
174: ionice : Set I/O scheduling class and priority.
175: hdparm : Tune hard disk drive parameters.
System Security
176: iptables : Configure firewall rules.
177: ufw : Uncomplicated Firewall for Ubuntu.
178: fail2ban : Protect against brute-force attacks.
179: clamscan : Scan for viruses and malware.
180: chkrootkit : Detect rootkits.
Package Management Tips
181: apt-get autoremove : Remove unused packages.
182: yum clean : Clean package cache.
183: dnf history : Manage transaction history (Fedora).
184: zypper clean : Clean package cache (openSUSE).
185: apt-get dist-upgrade : Perform a distribution upgrade.
Troubleshooting
186: strace : Trace system calls and signals.
187: lsof : List open files and processes.
188: netstat -tuln : Display open network ports.
189: ps aux : List all running processes.
190: dmesg | tail : Display kernel logs.
Command Line Shortcuts
191: Ctrl+C : Interrupt a running command.
192: Ctrl+Z : Suspend a command.
193: Ctrl+D : Logout or exit the terminal.
194: Ctrl+R : Search command history.
195: Tab Completion : Auto-complete commands.
Fun with ASCII Art
196: toilet : Create colorful text banners.
197: figlet : Generate ASCII text banners.
198: cowsay : Display talking cows.
199: sl (Steam Locomotive) : Watch a train go by!
200: fortune : Get a random fortune.
FAQs Linux commands cheat sheet
Can I use these commands on any Linux distribution?
Absolutely! These commands are universal and work across various Linux distributions.
Do I need to be a Linux expert to use these commands?
No, this list covers commands for all levels, from beginner to advanced users.
Are there any risks involved in using these commands?
Most commands are safe, but exercise caution when dealing with system-critical operations.
Can I automate tasks with these commands?
Certainly! Many of these commands can be used in scripts to automate repetitive tasks.
Where can I learn more about Linux?
Explore Tech Linux, others online tutorials, forums, and Linux documentation for in-depth learning.
Is Linux suitable for beginners?
Linux is user-friendly and beginner-friendly, with a supportive community like Techlinux.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve now explored a comprehensive Linux commands cheat sheet that covers essential commands and tasks. With these commands at your fingertips, you’ll be well on your way to mastering the Linux terminal. Keep practicing, and soon you’ll become a Linux command-line pro.